Function: Confocal
The Confocal function allows the acquisition of high-resolution confocal images, which is useful when dSTORM is not viable:
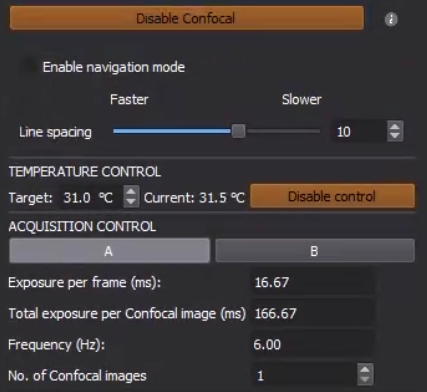
- Enable/Disable Confocal: enable/disable the confocal mode.
- Enable Navigation Mode: allow to quickly navigate the sample with minimal processing. The line-scan feature is disabled and therefore has no optical sectioning.
- Line Spacing (Faster or Slower): set the density of the "lines" (or patterns) projected onto the sample, which determines the number of frames acquired to reconstruct a confocal image.
- Exposure Per Frame (ms): set the exposure for each individual camera capture. This value will then be cast to a multiple of 16.66 ms, where the actual exposure is about 5.66 ms per frame. Multiple frames will be acquired to meet the total exposure requirement.
- Total Exposure Per Confocal Image (ms): set the total exposure for capturing each individual confocal image. Normally this value gets automatically updated as Exposure Per Frame * Line Spacing.
- Frequency (Hz): set the capture frequency per confocal image. Normally this value gets automatically updated as 1000 / Total Exposure Per Confocal Image.
- No. Of Confocal Image: set the number of confocal images to acquire.
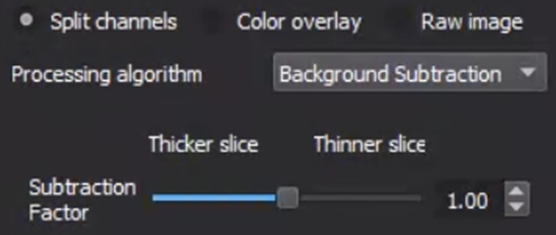
- Processing Algorithm: set the processing algorithm for reconstructing the confocal image to either Background Subtraction (default and recommended) or Standard Deviation.
- Subtraction Factor (Thicker Slice or Thinner Slice): set the subtraction factor for reconstructing the confocal image.
Instructions:
- Click on Enable Confocal to engage the DMD.
- Check Enable Navigation Mode and tune the laser power such that the sample is visible.
- Set the desired acquisition settings, including Line Spacing, Exposure Per Frame, and No. Of Confocal Images.
- Uncheck Enable Navigation Mode and Click on Acquire to start the acquisition.
- In Analyze, rerun the confocal processing with a different subtraction factor if needed:
Discussions:
- The ONI confocal is not a standard pinhole-based confocal but a DMD-based confocal.
- In confocal, the illumination intensity is lower due to the nature of structured illumination and mirror absorption. Lasers are switched off when engaging/disengaging confocal to avoid bleaching. Normally the laser power needs to be 3~4 times higher.
- In the navigation mode, even though the sample is fully illuminated, the intensity is not the same as that of normal illumination due to mirror absorption.
- Higher line spacing means more frames (or longer acquisition) and better resolution. It is recommended to be at least 7.
- The recommended subtraction factor is between 0.98 and 1.02.
Related Articles
Function: 3D
The 3D function uses a cylindrical lens to introduce a specific astigmatism pattern for 3D super-resolution imaging (not applicable to confocal or widefield). For detailed instructions on how to perform 3D Mapping Calibration, check here. ...Function: PythONI
What's PythONI? NimOS comes with its own python IDE called PythONI (/pi thon ni/). The simple python IDE allows you to write your own automation python script for controlling almost every part of the Nanoimager. This instruction will cover what's ...Function: FRET
The FRET function allows measuring distances at a single-molecule scale. For video instructions on how to use the FRET function, check here. If at any point you are having issues with the FRET process, please do not hesitate to contact the CX team.Function: ROI
The ROI function allows cropping a smaller area for imaging and recording: Draw ROI: draw to select the area (rectangle). Clear ROI: clear the current selection. Instructions Click on ROI to expand the tab. Click on Draw ROI and draw a rectangle on ...Function: TIRF
The TIRF function allows increasing the signal-to-noise ratio for super-resolution imaging. By default, the illumination on the Nanoimager is the same as epifluorescence wide-field microscopy. This corresponds to a degree of 0, in which light is ...